
 Scouting Structure Scouting Structure
 Scouting
is a non-political and non-military movement.
This is an adolescent and youth
movement that aims at creating responsible
and conscious, socially active and spiritually
strong, patriotic generation. The Scout method
of achieving this aim is a system of
self-education, which is provided in
small groups (patrols) through weekly gatherings, expeditions, jamborees,
etc. Scouting develops consciousness,
the desire of exploration and
disclosure. Scouts reveal the world outside
school, perceiving and sharing their
skills and knowledge with others. Scouting
is a voluntary, out-of-school, non-governmental
Organization.
Scouts take a constructive place in society
as responsible citizens and as members
of their local, national and international
community. Scouting
is a non-political and non-military movement.
This is an adolescent and youth
movement that aims at creating responsible
and conscious, socially active and spiritually
strong, patriotic generation. The Scout method
of achieving this aim is a system of
self-education, which is provided in
small groups (patrols) through weekly gatherings, expeditions, jamborees,
etc. Scouting develops consciousness,
the desire of exploration and
disclosure. Scouts reveal the world outside
school, perceiving and sharing their
skills and knowledge with others. Scouting
is a voluntary, out-of-school, non-governmental
Organization.
Scouts take a constructive place in society
as responsible citizens and as members
of their local, national and international
community.
Scouting and Guiding movements are
generally divided into sections by
age or school grade, allowing activities to be  tailored to the
maturity of the group's members.
These age divisions have varied over
time as they adapt to the local culture and environment. tailored to the
maturity of the group's members.
These age divisions have varied over
time as they adapt to the local culture and environment.
Scouting was originally developed for
youths between the ages of 11 and 17. In most member organizations,
this age group composes the Scout or Guide section. Programs were
developed to meet the needs of young children (generally ages 6 to
10) and young adults (originally 18 and older, and later up to 25).
Scouts and Guides were later split into "junior" and "senior" sections
in many member organizations, and some organizations dropped the
young adults' section. The exact age ranges for programs vary by
country and association. In Azerbaijan the age gradation is as follow:
6-12 Cub Scouts/ 12-18 Scouts / 18- above  Rovers and Leaders. Rovers and Leaders.
The World Organization of the Scout Movement (WOSM)
is the governing body of Scouting across the world. There are 160
National Scout Organizations that are Member of WOSM (World Organization
of Scout Movement)
The World Organization of the Scout
Movement (WOSM) is the Non-governmental international organization
which governs most national Scout Organizations, with 28 million
members. WOSM was established in 1920 and has its headquarters in
Geneva, Switzerland. It is the counterpart of the World Association
of Girl Guides and Girl Scouts (WAGGGS). The mission of WOSM is to
contribute to the education of young people, through a value system
based on the Scout Promise and Scout Law, to help build a better
world where people are self-fulfilled as individuals and play a constructive
role in society. WOSM is organized into regions and operates with
a conference, committee and bureau. Each region has number of member
countries.
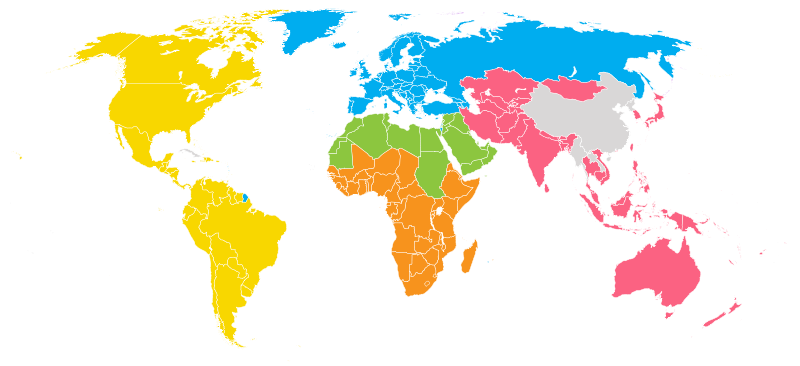
Scouting Regions
 Africa Africa
 Arab Arab
 Asia-Pacific Asia-Pacific
 Europe Europe
 Interamerica Interamerica
 Eurasia Eurasia
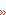
Eurasian Scout Region
The Eurasian Scout Region is the divisional
office of the World Scout Bureau
of the World Organization of the Scout Movement, headquartered
in Gurzuf near Yalta-Krasnokaminka,
Ukraine, with a branch office inMoscow.
All the formerly communist states of Central and Eastern Europe,
Central Asia. In 1997, WOSM
created the new Eurasian Region,
ostensibly to assist in the rebirth of Scouting in the 12 former
Soviet Republics: Armenia, Azerbaijan,
Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan,
Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan.
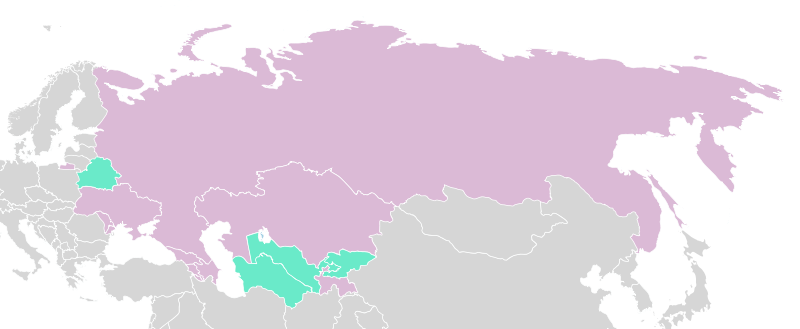
Scouting Division
 Scout
Regions Scout
Regions
 National Scout Organization National Scout Organization
 District District
 Groups Groups
 Troops/Units Troops/Units
 Patrols Patrols
 Scouts Scouts
 The
mission of Scouting The
mission of Scouting
 The mission of Scouting is to contribute to the education
of young people, through a value system
based on the Scout Promise and Law, to help build a better world
where people are self-fulfilled
as individuals and play a constructive
role in society. This is achieved by: The mission of Scouting is to contribute to the education
of young people, through a value system
based on the Scout Promise and Law, to help build a better world
where people are self-fulfilled
as individuals and play a constructive
role in society. This is achieved by:
involving them throughout their formative
years in a non-formal educational process
using a specific method that makes
each individual the principal agent of his or her development as
a self-reliant, supportive, responsible and committed person
assisting them to establish a value
system based upon spiritual, social and personal principles as expressed
in the Promise and Law.
The purpose of the strategy is to implement
the Mission. The adoption of the Mission in 1999 was a major milestone
for world Scouting. The mission and the six challenges identified
are essential to be addressed if our mission is to be achieved.
Six Challenges
Six challenges were identified at the
Durban Conference and need to be addressed to achieve our mission
are:
Relevance: meeting the needs and aspirations
of young people.
Complementary nature: focusing on the
distinctive contribution Scouting can make to the education of young
people, particularly through the Scout Method.
1. Membership: reaching out to more
young people.
2. Adults: attracting and retaining
the adults we need.
3. Relationships and partnerships:
working with others to better serve
young people.
4. Unity: pursuing a common purpose
at all levels.
The Three Strategic Areas
The six challenges provide three broad
areas of work: 
Young People: encompassing the challenges
on Relevance, Complementary nature and Membership in order to bring
better Scouting to more young people, especially adolescents.
Adults: encompassing the challenge
on Adults: attracting and retaining the adults we need, with an emphasis
on the concept of volunteering.
Structures and Systems: encompassing
the challenge on Relationships and
partnerships - which recognizes the need to work with others to serve
young people - and the challenge
on Unity: pursuing a common purpose
at all levels. Work in this strategic area should lead to an increase
in the overall effectiveness of the
Movement.
 The
Strategy The
Strategy The Strategy for Scouting responds
to the needs of Scouting because:
 It is based upon the mission of Scouting. It is based upon the mission of Scouting.
It takes into account the key challenges
which NSOs are facing in implementing the mission.
It proposes a shared vision of Scouting
for the 21st century.
It focuses on three main areas which
are crucial for the success of Scouting:
the needs and expectations of young
people,
the motivation of adult leaders to
contribute to the mission of Scouting,
new trends in managing non-governmental
organizations
It identifies and proposes seven strategic
priorities which should be used by each National Scout Organizations
to build up its own action plans.
It identifies clearly the areas on
which the world and regional bodies should focus in order to support
their associations.

National
Scout Organizations
160 National Scout Organizations
are members of the World Organization
of the Scout Movement. These are listed below. The newest
members joined on 1 July 2008: Cambodia,
Montenegro, Syrian Arab Republic
and Ukraine.
Of the 160 National Scout Organizations,
126 belong only to the World
Organization of the Scout Movement (WOSM), and 34 belong both
to WOSM and to The World Association
of Girl Guides and Girl Scouts
(WAGGGS).
Of the 126 National Scout Organizations
which belong only to WOSM, 100
are open to boys and girls in some or in all program sections.
20 are only for boys. All 34 National
Scout Organizations which belong
both to WOSM and to WAGGGS are open to boys and girls.
National members are encouraged
to notify the concerning the
creation of new web sites, or
changes in address. read
more



Jamboree,
Moot
The World Scout Jamboree is a Scouting jamboree
of the World Organization of the Scout Movement, typically attended by several
tens of thousands of Scouts from around the world, aged 14 to 17...
|

Joti,
Jota, Jott
Jamboree on the Air, known by its acronym JOTA, is an international Scouting
and Guiding activity held annually on the third full weekend in October.
|
|